04.6.13.20 zephyr-7b-beta-awq
Model description
The @hf/thebloke/zephyr-7b-beta-awq model includes two nodes:
- zephyr-7b-beta-awq Prompt (preview)
- zephyr-7b-beta-awq With History (preview)
Model ID: @hf/thebloke/zephyr-7b-beta-awq. The Zephyr 7B Beta AWQ is an efficient, accurate, and lightning fast low bit weight and quantization variant of the Zephyr model.
The Zephyr-7B-Beta-AWQ model is used to perform language-level tasks with high efficiency, accuracy, and speed. The main features of this model are:
Efficiency:
- The model uses low-bit weight quantization, which significantly reduces the model size and memory consumption.
- This makes the model more energy efficient and suitable for deployment on limited resources such as mobile devices or embedded systems.
Accuracy:
- Despite the use of low-bit quantization, the model maintains high accuracy on various language tasks.
- This is achieved through specific quantization techniques and model tuning.
Speed:
- The model is capable of performing language operations at high speed, which is important for real-time interactivity.
- Optimizing the model for low-bitrate processing allows for high performance.
These characteristics make the Zephyr-7B-Beta-AWQ useful in scenarios where efficient and fast language processing is required, such as mobile applications, embedded systems, resource-constrained cloud services, and other similar environments.
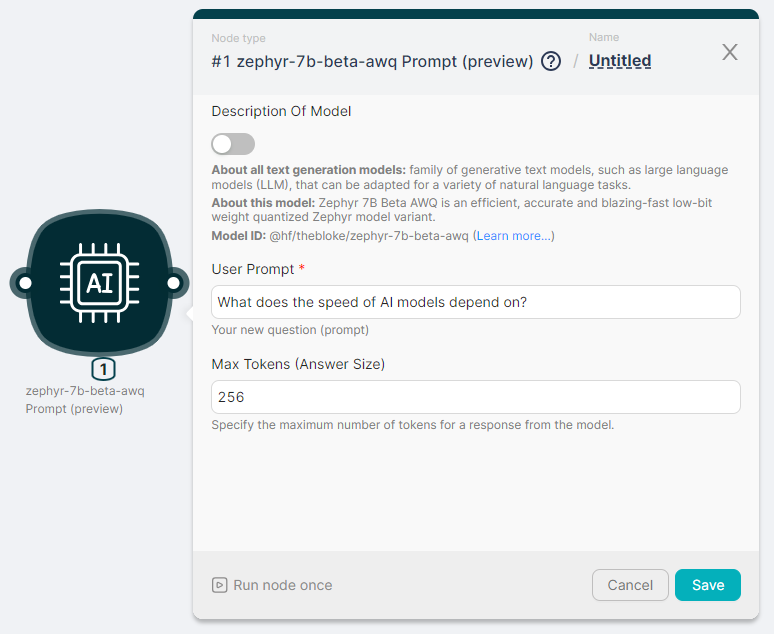
Example of launching a node
A description of the node fields can be found here.
Let's run the zephyr-7b-beta-awq Prompt (preview) node to process the text and generate a response with parameters:
- User Prompt - What does the speed of AI models depend on?;
- Max Tokens (Answer Size) - 256.
The output of the node execution is JSON:

- with a response to the
"response"request;
- with the status of the action
"success": true.
JSON
{
"result": {
"errors": [],
"messages": [],
"result": {
"response": "The speed of AI models depends on several factors, including:\n\n1. Model architecture: The design of the neural network, including the number of layers, the type of activation functions, and the size of the filters, can significantly impact the computational complexity and training time of the model.\n\n2. Dataset size: The larger the dataset, the more data the model needs to process, which can increase the training time.\n\n3. Hardware: The performance of the AI model also depends on the hardware used to train and run it. High-performance GPUs and specialized AI processors can significantly accelerate the training and inference times.\n\n4. Optimization techniques: Various optimization techniques, such as stochastic gradient descent, can help to speed up the training process by reducing the number of iterations required to converge.\n\n5. Data augmentation: By artificially increasing the size of the dataset through techniques such as flipping, cropping, and rotating images, data augmentation can help to improve the model's performance and reduce overfitting, which can lead to faster training times.\n\n6. Transfer learning: Pre-trained models can be used as a starting point for new tasks"
},
"success": true
}
}