12.06 Using Iterator node
As an example of how the Iterator node works, let's create a scenario that results in recording two variables and their values equal to the elements of an array of numbers.
Five nodes must be added for the scenario to work successfully:
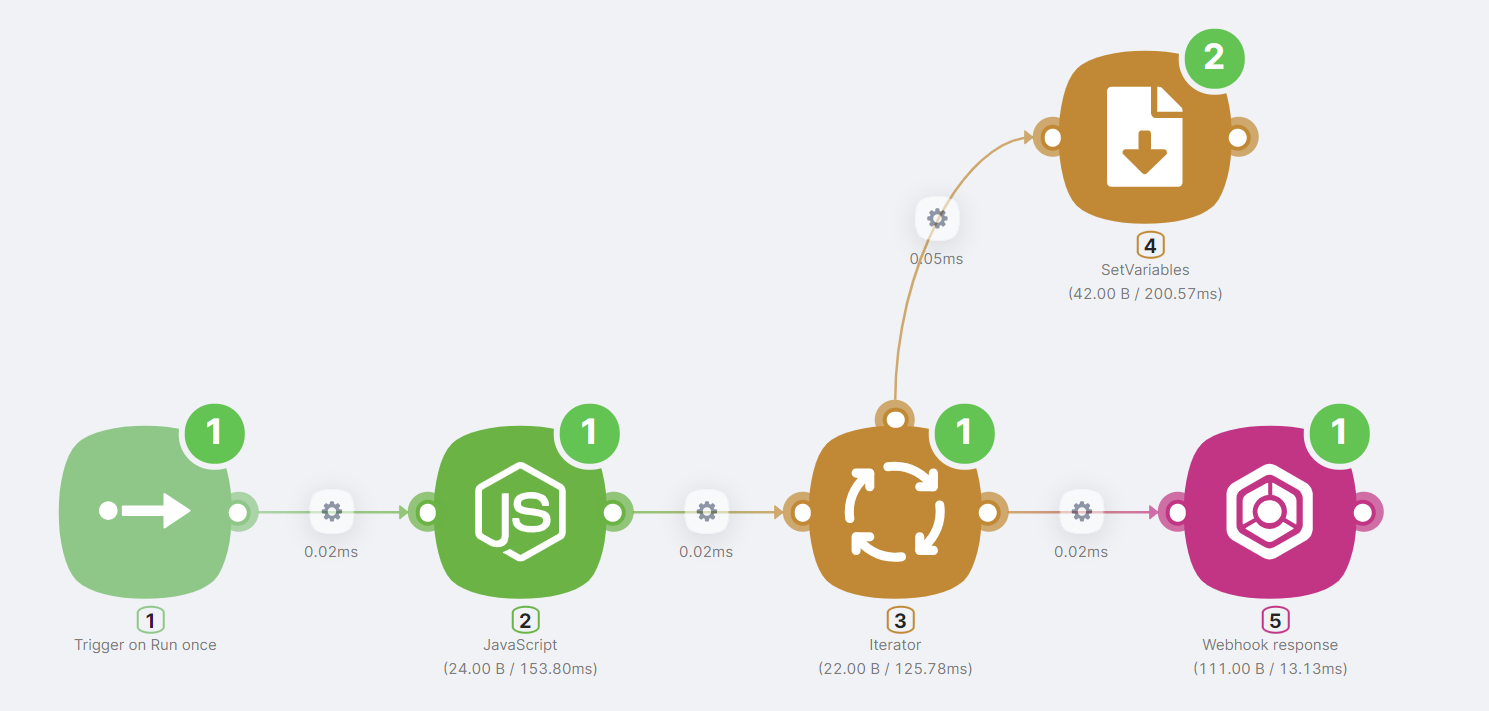
- (1) Trigger on Run once node to run a scenario after clicking on the Run once button;
- (2) JavaScript node with code to produce an array of two random numbers.
export default async function run({execution_id, input, data}) {
const randomNumbersArray = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
randomNumbersArray.push(Math.floor(Math.random() * 100));
}
return {
randomNumbers: randomNumbersArray
};
}
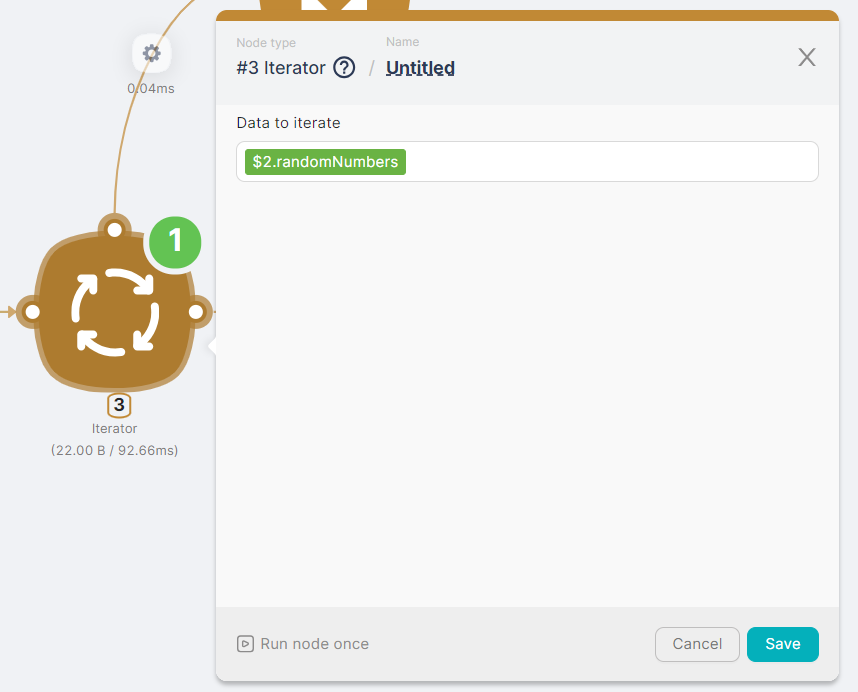
- (3) Iterator node to take the array generated in the JavaScript node and process it sequentially.
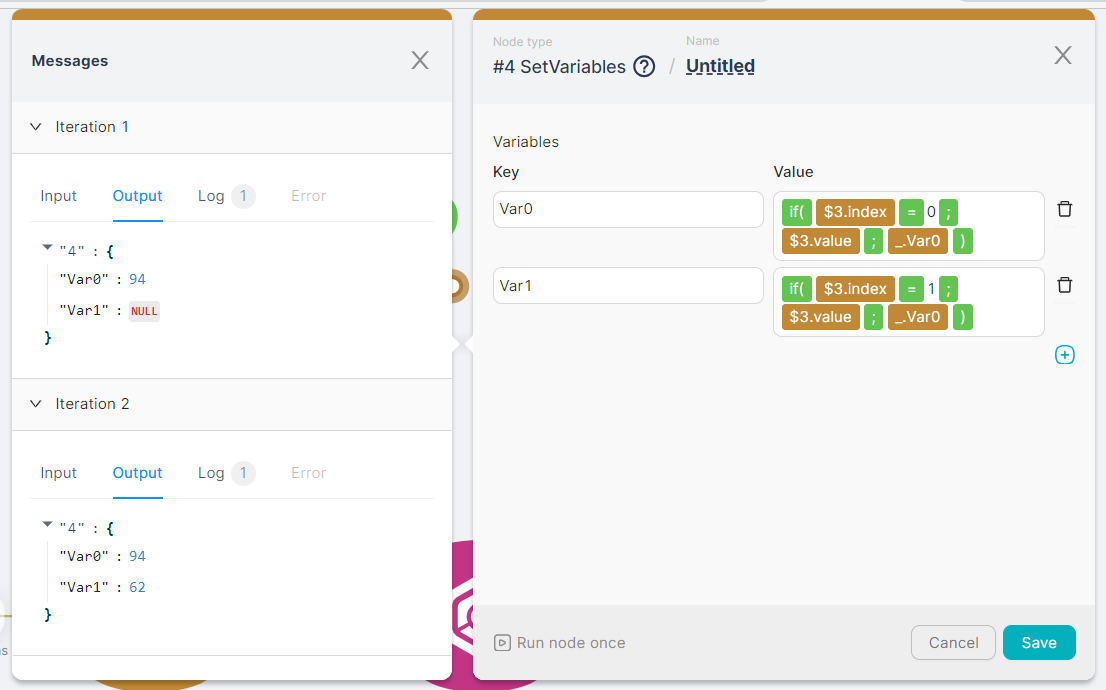
- (4) SetVariables node for writing two variables and their values according to the numbers in the array. For the first variable
Var0, the value of the first number of the array is written, or if another part of the array is being processed, the current value is overwritten. For the second variableVar1, the value of the second number of the array is written, or if another part of the array is being processed, the current value is overwritten.
- (5) Webhook response node to generate a summary of the scenario execution.
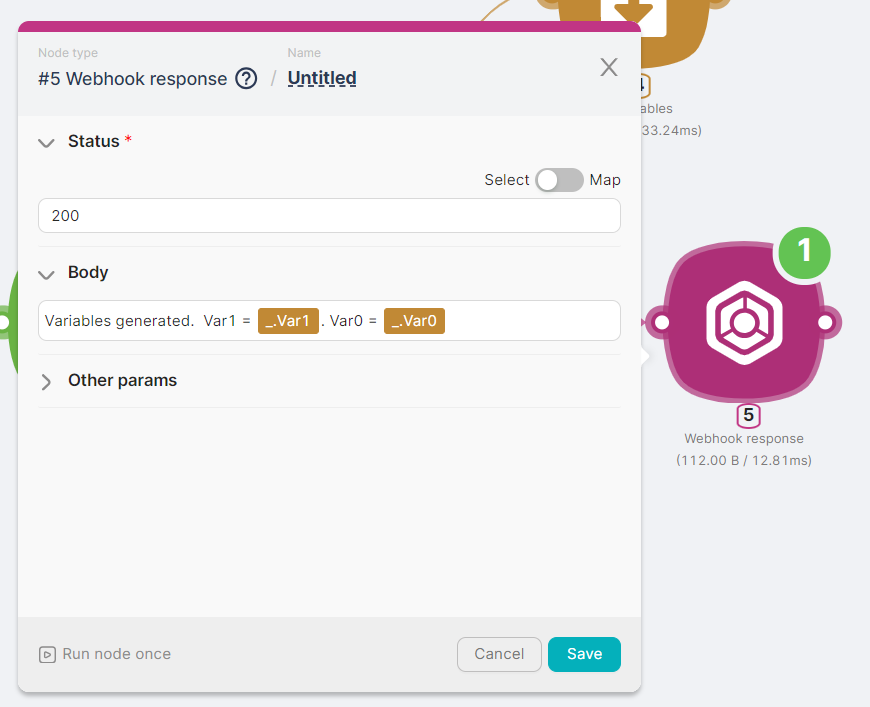
The outcome of the scenario is a response generated by the Webhook response node and two variables that can be used in the scenario.